Mass Spectrometry Facility
Mass spectrometry Facility
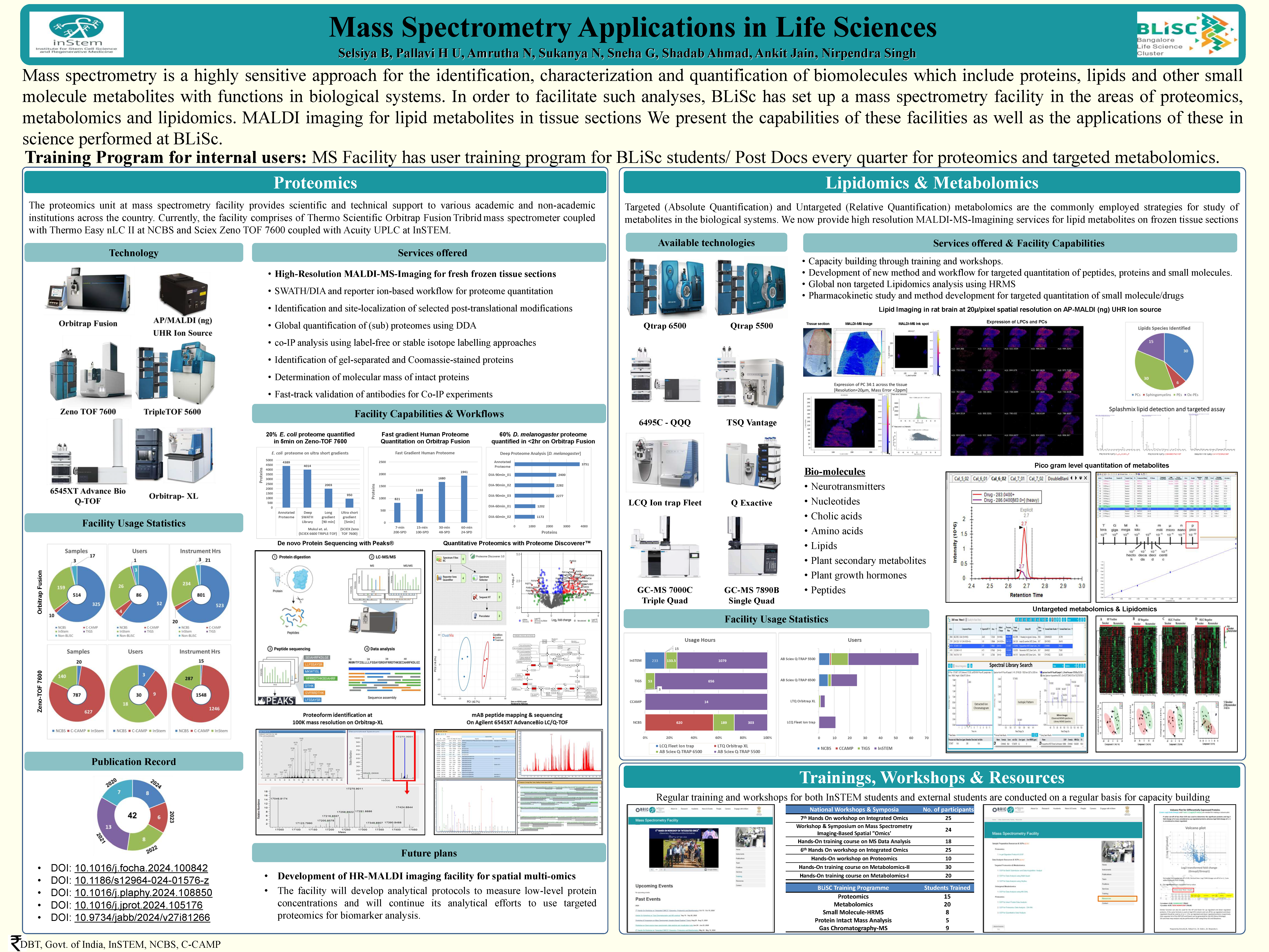
The mass spectrometry (MS) resources on campus aim to provide researchers with state-of-the-art techniques and equipment to characterize biomolecules including proteins and peptides (Proteomics), glycans and their conjugates (Glycomics & glycoproteomics), metabolites (Metabolomics) and lipids (Lipidomics). A number of state-of-the-art instruments for the separation, identification and quantitation of all major biomolecules by mass spectrometry based approaches are available. In addition to providing MS based structural characterization services, the mass spectrometry facility on the Bangalore Life Science Cluster campus provides training to on-campus students, postdocs and researchers on the use of different LC-MS/MS technologies as well as develop new analytical methods required to be on cutting-edge and to facilitate on-campus research.
There are four MS units operate under the facility to be able to provide expertise training and services in each of the different ‘-omics’ platforms.
1) Proteomics
2) Small molecule Mass spectrometry
MS facility is driven to establish a hyphenated Mass Spectrometry based small molecule analysis platform in basic biology, clinical studies and biotechnology at Bangalore Life Sciences Cluster (BLiSc) affiliated institutes; NCBS, CCAMP and InStem. The platform undertakes clinical, biological, chemical, ecology studies of lipidomics/ metabolites for BLiSc community and external researchers. Direct infusion as well as LC-MS/MS methods using HRMS like Orbitrap technology (Orbitrap Fusion, Q-Exactive, Orbitrap XL) are available.
Identification and quantification of known and unknown Proteins/ Peptides Lipids/metabolites in biological fluids such as plasma, urine, saliva and tissue using Data dependant (DDA) and data independent (DIA) analysis for the estimation of lipids and other metabolites. Comprehensive lipid profiling and quantitation is a system-based study of all possible lipid classes in the biological system. Phosphoinositides measurements in cell signaling.