Search Bar
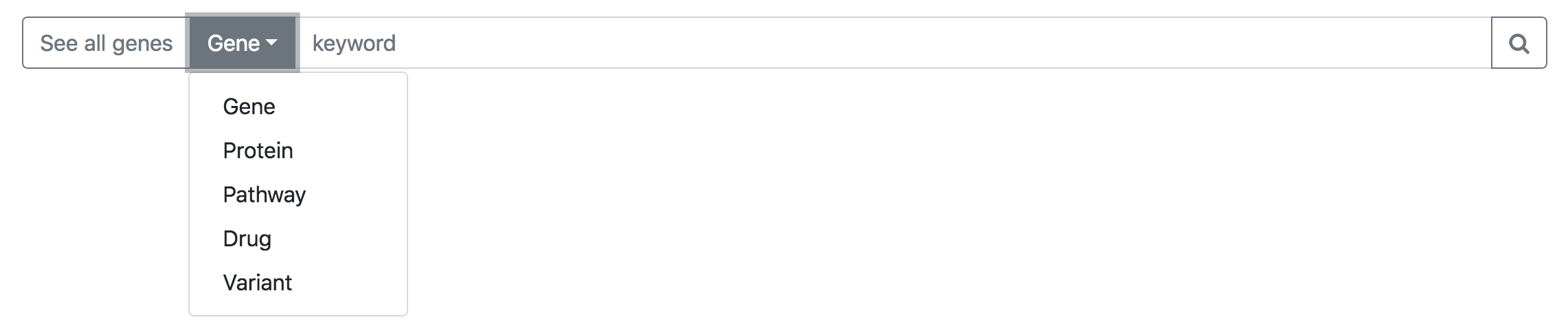
- See all genes - Lists all the genes that causes any of the three types of cardiomyopathy :
- HCM - Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- DCM - Dialated cardiomyopathy
- ARVC - Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy
-
Dropdown Menu - Search can be specified through different options in the dropdown.
Each options lets you search the following keywords:
Keyword Search terms Gene Official gene symbol (Eg: ACTC1), Ensembl ID (Eg: ENSG00000159251), and gene synonyms (Eg: ACTC) Protein Uniprot ID (Eg: P68032), protein name (Eg: Actin, alpha cardiac muscle 1 ) Pathway Pathway name (Eg: Cardiac muscle contraction - Homo sapiens (human)) Drug Drug name (Eg: Metoprolol), drug type (Eg: Beta Blockers (Beta-Adrenergic Blocking Agents)) , drug bank ID (Eg: DB00264) Variant HGVSc (Eg: c.1028delC), HGVSp (Eg: p.Thr343Metfs), rs ID (Eg: rs730880686)
Gene page

Each tab gives you information regarding different aspects of the gene.
Basic
The basic page give details about the gene and protein.
Gene Ontology
The GO defines concepts/classes used to describe gene function, and relationships between these concepts. It classifies functions along three aspects:
- Molecular function - molecular activities of gene products
- Cellular component - where gene products are active
- Biological process - pathways and larger processes made up of the activities of multiple gene products.
Variant Information (ExAC)
Each variant of the gene is shown that is availiable in ExAc. All data are based on GRCh37/hg19
Variant Information (NHLBI)
Each variant of the gene is shown that is availiable in EVS (Exome Variant Server).
- Variant GRCh37 Pos - Chromosome no : position on chromosome based on GRCh37/hg19
- rs ID - It is an identification tag assigned by NCBI to a group (or cluster) of SNPs that map to an identical location
- EA Genotype # - The observed genotype counts for the listed genotypes in European American population (delimited by /). For INDELs, the alleles are listed with aliases, such as, A1, A2, or An referring to the N-th alternate allele while R refers to the reference allele.
- AA Genotype # - The observed genotype counts for the listed genotypes in African American population (delimited by /). For INDELs, the alleles are listed with aliases, such as, A1, A2, or An referring to the N-th alternate allele while R refers to the reference allele.
- All Genotype # - The observed genotype counts for the listed alleles in all populations (delimited by /). For INDELs, the alleles are listed with aliases, such as, A1, A2, or An referring to the N-th alternate allele while R refers to the reference allele.
- MAF (%) (EA/AA/All)- the minor-allele frequency in percent listed in the order of European American (EA), African American(AA) and all populations (All) (delimited by /). For the multi-allelic variants, the MAF is defined as the allele frequency in percent for all the minor alleles.
- GVS Function - the GVS functions are calculated locally and stored in our local database; they are based on the alleles for all populations and individuals; the bases in the coding region are divided into codons (if a multiple of 3), and the resulting amino acids are examined:
- intergenic: between genes
- intron: in an intron region
- near-gene-3: near the 3' end of a gene
- near-gene-5: near the 5' end of a gene
- utr-3: in a 3'-utr region
- utr-5: in a 5'-utr region
- coding-notMod3: in a coding region leading to an ambiguous assignment of synonymous versus nonsynonymous
- coding-synonymous: leading to no amino acid change
- splice-3: in the 3' end of a splice site
- splice-5: in the 5' end of a splice site
- missense: leading to an amino acid change
- stop-lost: leading to a loss of a stop codon
- stop-gained: leading to a gain of a stop codon
- coding (INDEL): in a coding region with the number of base changes a multiple of 3
- codingComplex (INDEL): indel spanning through more than one exon involving a coding region
- frameshift (INDEL): in a coding region with the number of base changes not a multiple of 3
- cDNA Change - Variant represented in the HGVS notation at the coding DNA level for a transcript
- Protein Change - A protein change represented in the HGVS notation is translated based on the specific transcript listed in the column of "mRNA Accession".
- PolyPhen2 (Class:Score) - Prediction of possible impact of an amino acid substitution on protein structure and function based on Polymorphism Phenotyping (PolyPhen2) program. It lists both the PolyPhen2 prediction class and the PolyPhen2 score separated by a ":".
Clinical Information
Clinical information obtained from Clinvar.The chromosome base position is on GRCh37/hg19. Each column represents
- HGVSc - the HGVS coding sequence name. More details can be found https://www.hgvs.org/mutnomen/recs-DNA.html
- HGVSp - the HGVS protein sequence name
- Type -
- Phenotype List - Disease or trait associated with a variant.
- Clinical significance - Theclinical significance reported by submitters. This may be different from theoverall clinical significance for the variation. For example, if you limit your results to Pathogenic , the results include all variations with a submitted interpretation of Pathogenic on an SCV. The overall clinical significance for the variation may be Pathogenic, Likely pathogenic/Pathogenic, or conflicting interpretations of pathogenicity.
- Phenotype IDs -
- rs ID -
Phenotype
The Mammalian Phenotype Ontology (MP), for classifying and organizing phenotypic information related to the mouse and other mammalian species.
Pathways
The pathways that is involved with the gene.
PPI
The network shows all the interacting proteins. Different labels are given for cardiomyopathy genes, human genes and other organisms
Drug
Drugs targeting this proteins is shown in this network.
API
Data can also be accessed via an API https://graphiql-online.com/. The end point should be given as https://www.instem.res.in/cardiodatabase/v1alpha1/graphql. Data can be accessed by giving graphQL queries.